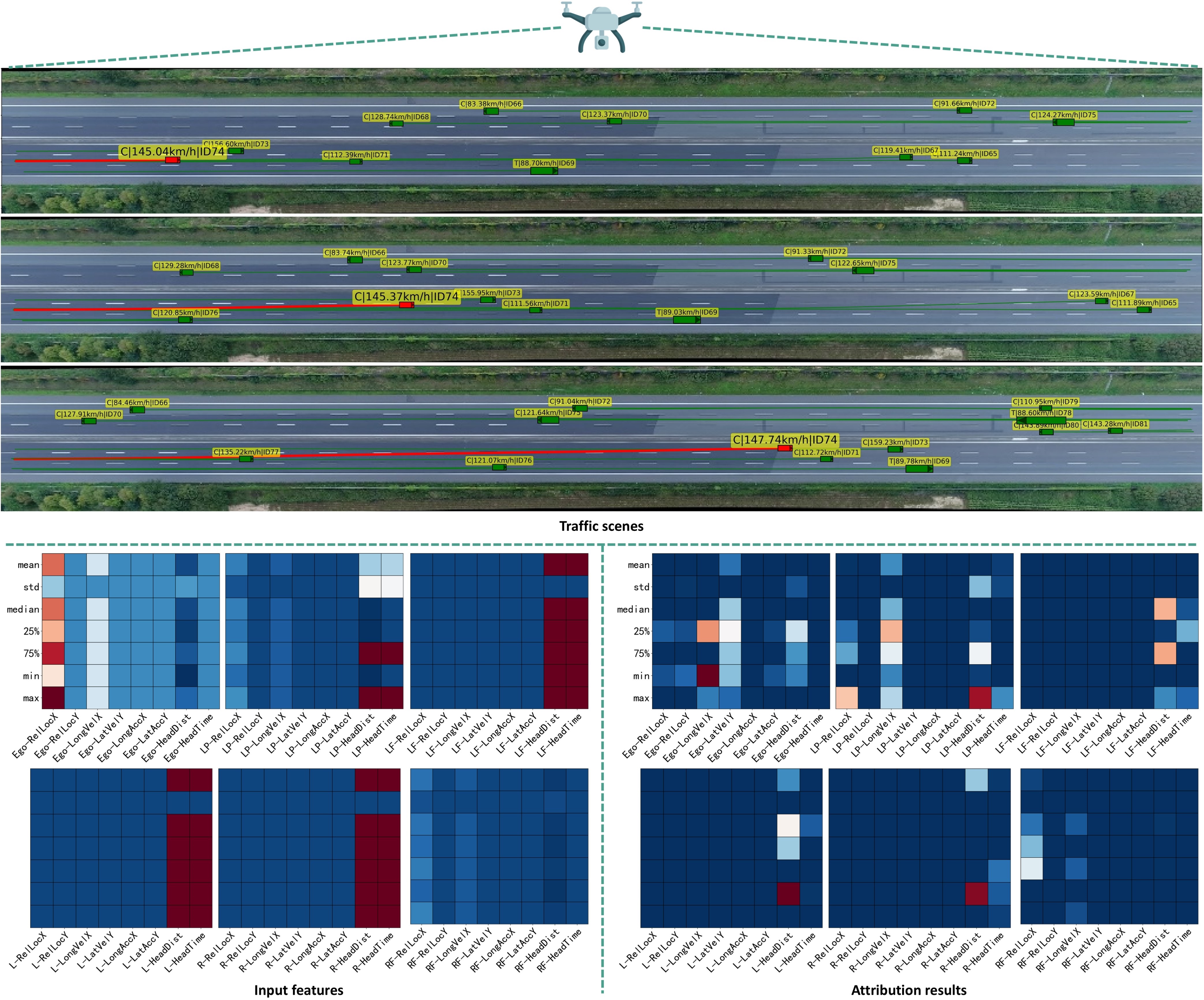
Multiple Traffic Scene Attribution
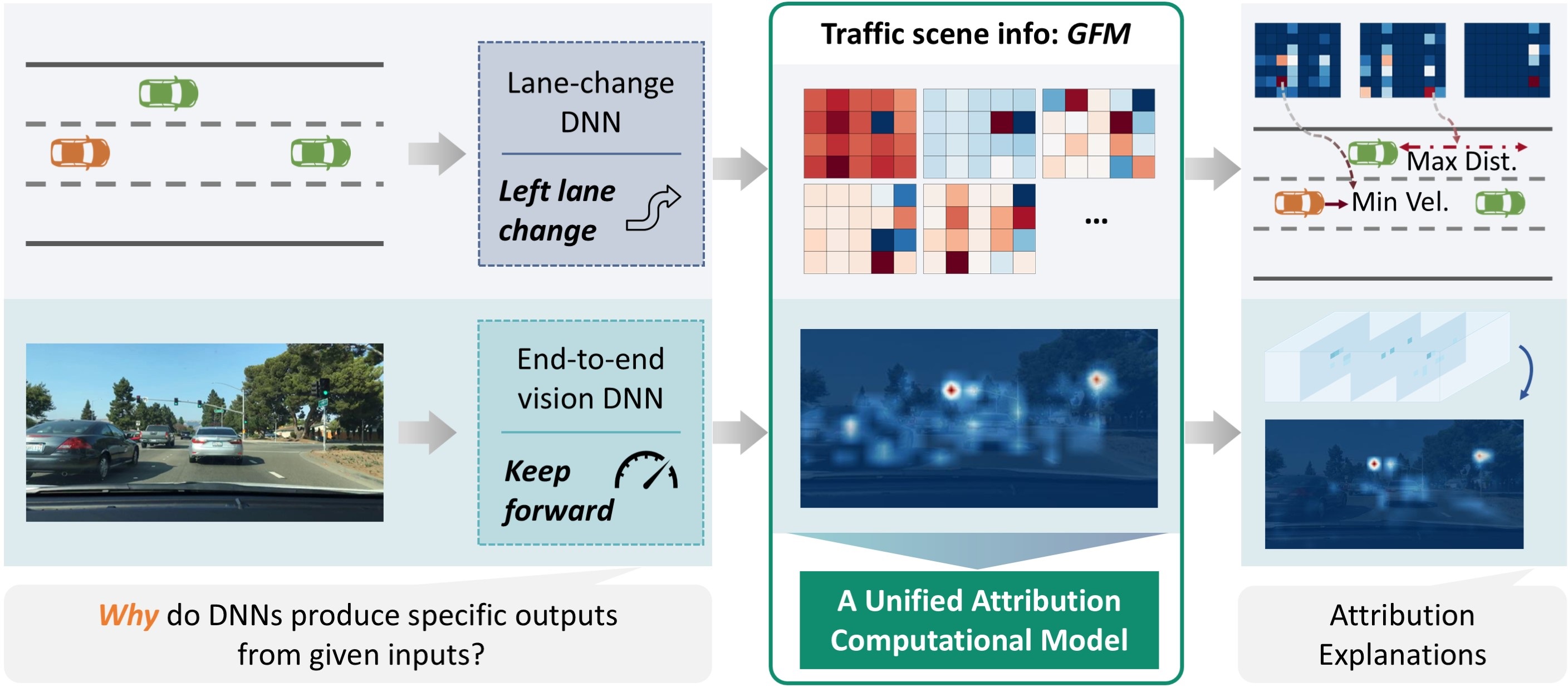
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have advanced autonomous driving, but their lack of transparency remains a major obstacle to real-world application. Attribution methods, which aim to explain DNN decisions, offer a potential solution. However, existing methods, primarily designed for image classification models, often suffer from performance degradation and require specialized algorithmic adjustments when applied to the diverse models in autonomous driving. To address this challenge, we introduce a universally applicable representation of traffic scenes, forming the basis for our unified attribution method. Specifically, we leverage the first-order Taylor expansion at a specific hidden layer, i.e., the product of gradients and feature maps, to represent abstract traffic scene information. The traffic scene information and corresponding hidden features inform both the integration path generation and the starting point optimization for computing Aumann-Shapley attributions. These components enable consistent and effective explanations across both lane-change and vision-based models without requiring model-specific modifications. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results, conducted on two distinct model types, demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to state-of-the-art techniques.
Article
“Traffic Scene-Informed Attribution of Autonomous Driving Decisions.” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Article GitHub Repo
